Analysis
Standard Chartered Advances Adaptation Finance as ClimateAligned Research Shows Africa Leading the Way
Analysis for sustainable finance professionals and climate resilience investors
Apr 3, 2025 @ London
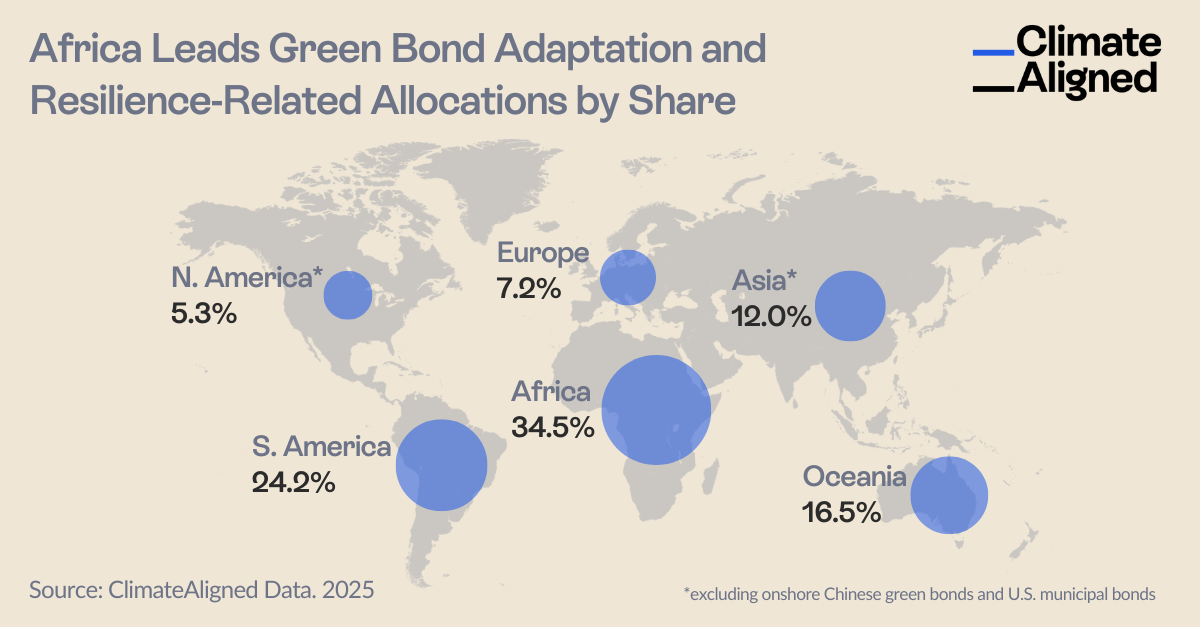
As Standard Chartered completes its first corporate adaptation finance deal, ClimateAligned data reveals Africa already allocates 34.5% of its labelled use of proceeds bonds to climate resilience— the highest proportion globally.
As Standard Chartered scales up its adaptation finance initiatives amid global economic losses exceeding $2 trillion from extreme weather, ClimateAligned's research reveals Africa is already leading the way in climate resilience investments.
Standard Chartered Pioneers Corporate Adaptation Finance
Standard Chartered's recent completion of an adaptation finance transaction for JinkoSolar marks a significant step forward for the market, facilitating the delivery of storm and extreme weather-resilient solar modules to locations vulnerable to tornadoes, tropical storms, and sandstorms in the US, UAE, and Saudi Arabia.
This milestone transaction follows the bank's launch of the breakthrough Guide for Adaptation and Resilience Finance, which mapped over 100 investable activities in this emerging field. The deal demonstrates the commercial viability of adaptation as an asset class while addressing urgent infrastructure resilience needs in regions facing escalating climate impacts.
Africa Already Leading in Adaptation Finance: ClimateAligned Research
Using ClimateAligned's analytics platform, we analysed a sample of allocation data from green and sustainable bonds worth over $940 billion globally and discovered a compelling regional story: While Africa receives just a small fraction of global sustainable finance flows, it dedicates a remarkable 34.5% of this capital to adaptation and resilience projects—proportionally the highest commitment worldwide. In second place, was South America, with 24.2% of sustainable bond proceeds allocated towards adaptation and resilience projects.
Europe and North America fell short, with just 7.2% and 5.3% of sustainable bond proceeds respectively allocated towards adaptation and resilience projects.
 Source: ClimateAligned Data, 2025
Source: ClimateAligned Data, 2025
Overall, 8.3% of global sustainable bond proceeds analysed ($940.5 billion) support adaptation and resilience initiatives, highlighting significant growth potential in this investment category.
Development Banks: Dominating Africa's Adaptation Finance Landscape
The capital flows in Africa's adaptation investments are overwhelmingly driven by multilateral development banks, which account for the vast majority of dollar value in our sample. Unlike Asia, Europe, and Oceania—where private companies and municipalities contribute significantly to sustainable finance—Africa's adaptation portfolio is predominantly shaped by institutions like the French Development Agency (AFD), which has strategically prioritised climate adaptation and sustainable land use across the continent, with notable investments in countries Egypt, Côte d'Ivoire, and Mauritius.
This institutional dominance creates a distinctive investment profile compared to other regions and reflects the development banks' nuanced understanding of regional climate vulnerabilities and priorities, channelling capital toward projects that build resilience against increasingly severe climate impacts. The relative absence of private sector and municipal issuers highlights both a challenge and opportunity for broadening participation in Africa's adaptation finance market—potentially through corporate adaptation frameworks like Standard Chartered's recent initiative.
South America: Strong Second in Adaptation Priorities
South America ranks second in adaptation finance, allocating 24.2% of its sustainable bond proceeds to resilience initiatives. However, like Africa, these percentages are influenced by a relatively small overall sample size.
The Central American Bank for Economic Integration has been instrumental, focusing on sustainable water management in Nicaragua, Costa Rica, El Salvador, and Honduras. These investments address critical climate vulnerabilities in a region facing increasing water stress and flooding risks.
South America's approach demonstrates meaningful commitment to resilience, particularly in water security, offering relevant models for adaptation finance in middle-income countries.
Standard Chartered and the Future of Adaptation Finance
Standard Chartered's approach represents a significant market evolution, particularly for corporate clients. As Marisa Drew, Chief Sustainability Officer at Standard Chartered, noted when launching their adaptation framework: "We set out to provide the clarity needed across the market to accelerate investment into adaptation and resilience."
The bank's recent JinkoSolar deal demonstrates how adaptation finance can address concrete climate vulnerabilities in diverse geographies, from hurricane-prone Florida to sandstorm-affected regions in the Middle East. This practical application of resilience financing shows how targeted investments can mitigate economic risks while supporting clean energy deployment.
The Adaptation-Nature Nexus
Africa's leadership is unsurprising. Adaptation finance (34.5%) has strong overlap with nature-related investments. As previous ClimateAligned research found, 24.0% of Africa's sustainable bond proceeds are allocated towards nature-related investments. Climate resilience projects are those particularly those focused on climate change adaptation directly, but also include water management and sustainable agriculture.
This integrated approach recognises the fundamental role of healthy ecosystems in buffering communities against climate impacts, from coastal mangroves that reduce flood risks to sustainable land management practices that enhance agricultural resilience.
Market Implications for Investors
For sustainable finance professionals navigating this evolving landscape, the convergence of Standard Chartered's corporate initiative with Africa's existing adaptation leadership offers several strategic insights:
- Untapped private investment potential. The near-absence of private companies in Africa's adaptation finance landscape represents an enormous growth opportunity, particularly as Standard Chartered's framework demonstrates how corporate adaptation finance can work in practice.
- Vulnerability-investment mismatch. Many African nations face acute climate vulnerabilities yet receive minimal adaptation finance flows—creating both impact and investment opportunities in regions where resilience needs are greatest.
- Market-defining frameworks. Standard Chartered's Guide for Adaptation and Resilience Finance provides needed clarity for identifying qualifying investments, potentially bridging the gap between development bank-led approaches and corporate adaptation finance.
Convergence of Approaches: The Path Forward
As climate impacts intensify—exemplified by the Los Angeles wildfires earlier this year and severe flooding in Dubai—adaptation finance represents not just a strategic investment opportunity but an economic imperative. Standard Chartered's corporate adaptation framework, combined with Africa's proven leadership in prioritising resilience through development finance, offers complementary models for addressing climate vulnerabilities.
While Africa's adaptation finance market shows impressive proportional commitment to resilience, its concentration among development banks highlights the opportunity to diversify the issuer base. Standard Chartered's work with corporate clients like JinkoSolar demonstrates how private sector participation—which features more prominently in Asia, Europe, and Oceania's sustainable finance landscapes—could unlock additional capital while maintaining a focus on concrete resilience outcomes.
For investors seeking alignment with real-world resilience needs, the convergence of Standard Chartered's corporate adaptation framework with Africa's established leadership in development bank-led resilience finance illuminates multiple pathways toward investment strategies that respond directly to our changing climate reality.
ClimateAligned's technology captures pre- and post-issuance allocation data at scale and in real time, providing the transparency investors need to drive capital where it's needed most.